Now that you have come to see the complete five types of overcurrent relays, Let’s first understand in short what is an overcurrent relay and where it is mainly used?
Definition of Overcurrent Relay: Overcurrent relay is a protective relay that operates when the load current exceeds a preset value.
The value of a current above which the relay will operate is called the pick-up value. It is the most common protection relay and is the cheapest among all other relays. Over Current relay is mainly used for the protection of different parts of the power systems such as distribution lines, large motors, power equipment, and other industrial systems, etc.
Types of Overcurrent Relays
The term “Overcurrent” is all about the current and time. There are five types of overcurrent relay based on current-time characteristics. They are:–
1. Definite-time overcurrent relay
2. Inverse-time overcurrent relay
3. Instantaneous Overcurrent Relay
4. Inverse Definite Minimum Time Overcurrent (I.D.M.T) Relay
5. Very Inverse-time Overcurrent Relay
6. Extremely Inverse-time Overcurrent Relay
Also learn: What is Electromagnetic Relays? Working Principle & Types
Definite-time Overcurrent Relay
In a definite-time overcurrent relay, the relay will operate when the current reaches its pick-up value and predetermined time. Here, the time for tripping when the current exceeds the pickup value is set and programmed.
The time-current characteristic curve for this type of relay is shown below.
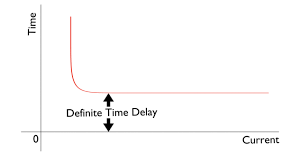
- The operating time is always constant, irrespective of the magnitude of the current above the pick-up value.
- An intentional time-delay mechanism is provided in the relay unit in order to set the definite operating time.
Inverse-time Overcurrent Relay
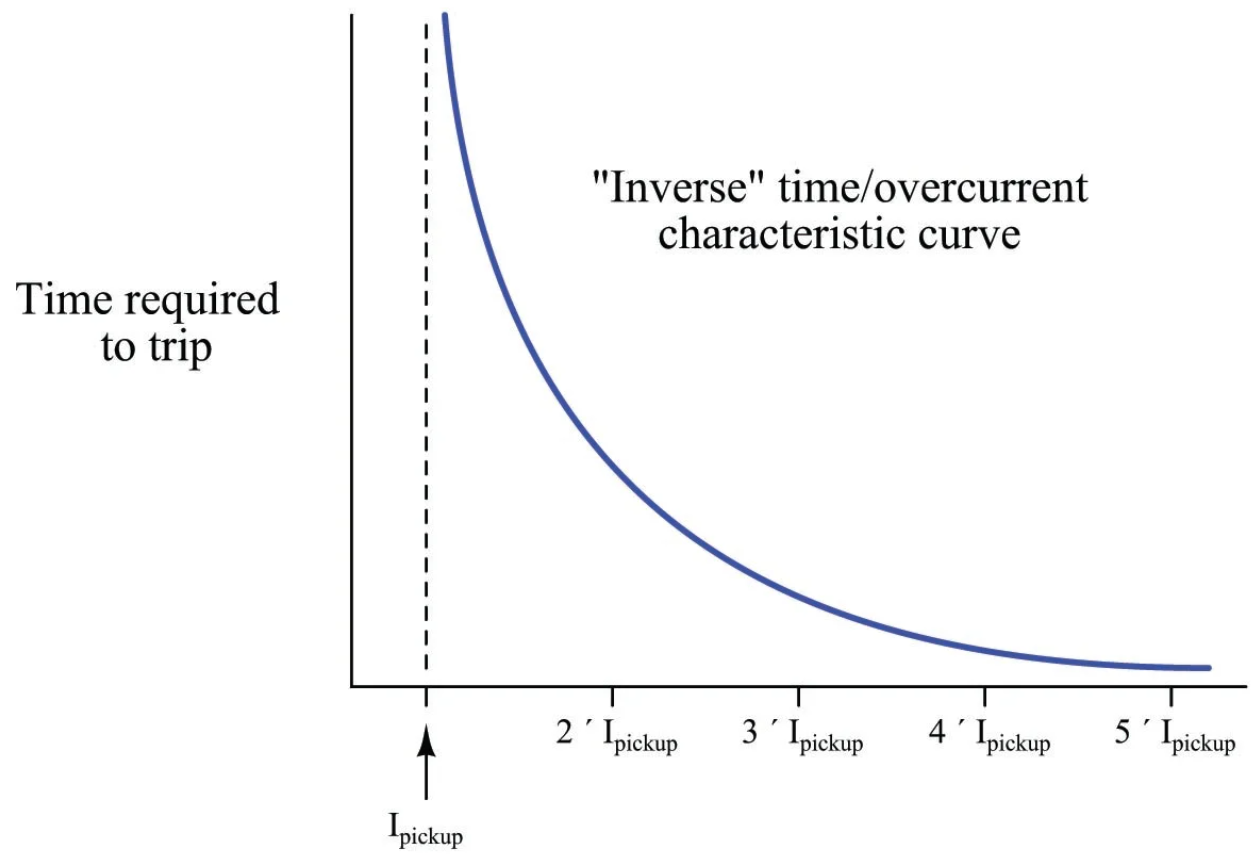
In inverse-time overcurrent relay, the relay operates only when the current exceeds its pick-up value. The operating time in this type of relay depends on the magnitude of the operating current. Here, if the operating time decreases as the current increases and vice-versa.
Instantaneous Overcurrent Relay
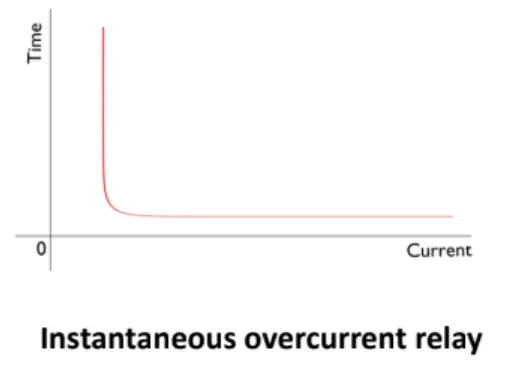
An instantaneous relay operates in a definite time and operates as soon as the current reaches the preset value. It is sometimes known as “high set” or “high speed” for its fast operation that works less than 0.1 seconds. Here the operating time is constant and doesn’t depend on the magnitude of the current.
Also see: Vacuum Circuit Breaker: Construction, Working & Applications
Inverse Definite Minimum Time Overcurrent (I.D.M.T) Relay

I.D.M.T relay gives an inverse-time current characteristic at lower values of the fault current and a definite-time characteristic at higher values of the fault current. I.D.M.T. relays are mainly used for the protection of distribution lines.
Generally, when the plug setting multiplier is below 10, then inverse characteristics is obtained. And, when the values of the plug setting multiplier are between 10 and 20, then the line in the graph tends to become a straight line, which will be towards the definite-time characteristic.
Very Inverse-time Overcurrent Relay

A very inverse-time overcurrent gives more inverse characteristics than that of a normal inverse relay or the I.D.M.T. relay. In very inverse-time overcurrent, time-current characteristic lies between a characteristic of I.D.M.T (curve ‘a’) and extremely inverse characteristic (curve ‘c’), as shown in the figure. The very inverse relay is mostly preferred when the I.D.M.T relay fails to operate.
The Very inverse time-current relays are preferred where there is a substantial reduction of fault current as the distance from the power source increases. Due to the steep characteristic of ‘very inverse-time overcurrent relay,’ it is more effective with ground faults.
Also see: What is an Electrical Fault? Definition, Types, Nature & Cause, its Effects, and statistics.
Extremely Inverse-time Overcurrent Relay
In an extremely inverse time overcurrent relay, the relay gives a time-current characteristic more inverse than that of the inverse and I.D.M.T. relays as shown in the figure below:

Extremely inverse relays are used when I.D.M.T. and inverse relays fail in a particular application. When the electromagnetic relay shows quick rising and falling of time-current characteristics, it can be termed as an extremely inverse relay.
The time-current characteristic of an extremely inverse relay is I^2t = K. In general, the extremely inverse relay characteristic is not good enough to be graded with fuses. But with electromechanical relay, it is good to use extremely inverse relays to grade with fuses.
An extremely inverse relay is used for the protection of machines against overheating. Therefore, this type of relays is used for the protection of power transformers, alternators, earthing transformers, expensive cables, railways trolley wires, etc.