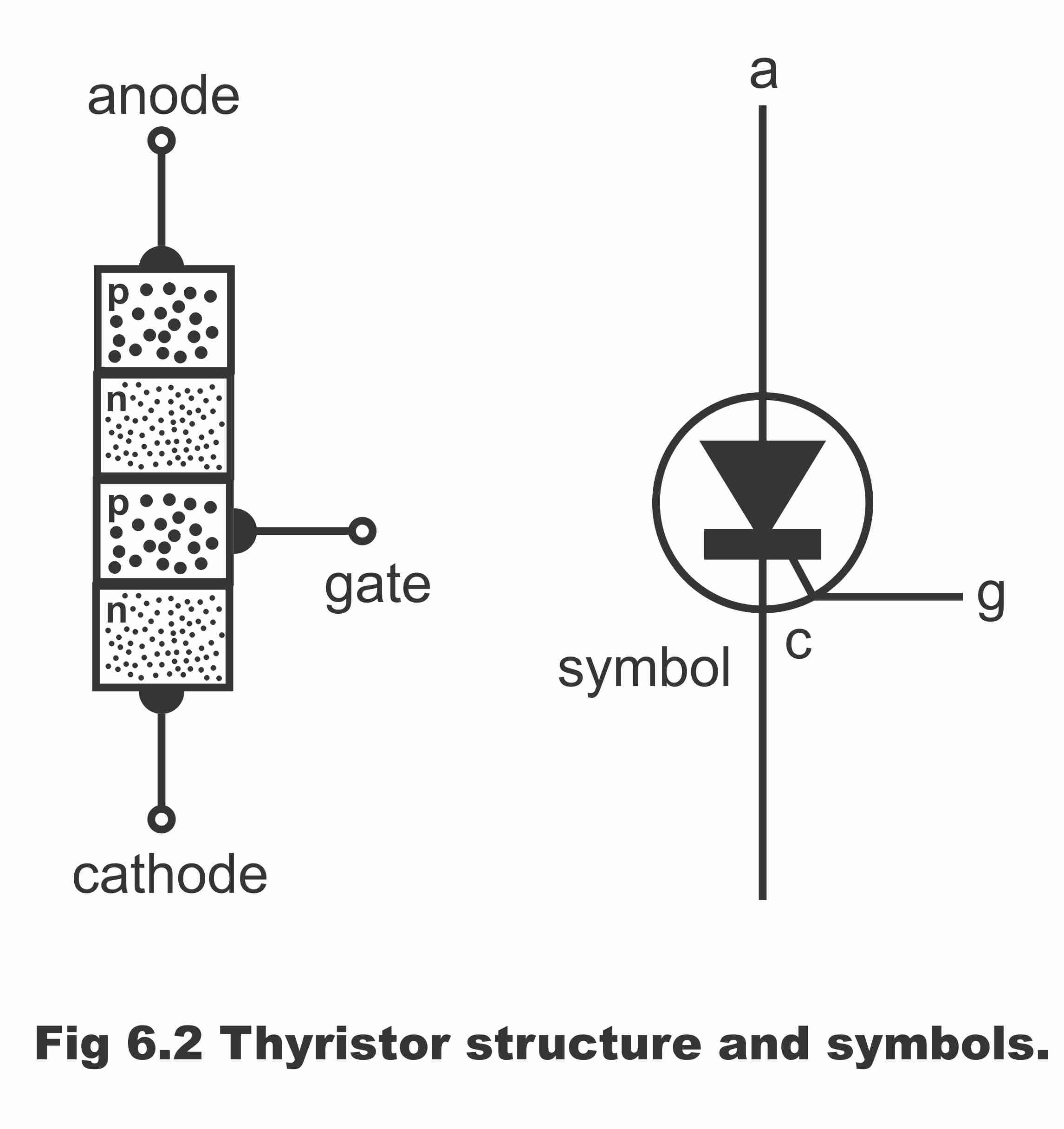
Thyristor triggering methods refer to the various techniques used to initiate the conduction of current through a thyristor, a semiconductor device that acts as a switch in electrical circuits. Mainly a thyristor is turned on by increasing the anode current.
Remember that the choice of triggering method depends on the specific application requirements, such as the required turn-on time, voltage and current ratings, and isolation requirements. This can be accomplished in one of the following methods.
1. Thermals: If the temperature of the thyristor is high, there is an increase in the number of electron-hole pairs, which increases the leakage currents. This increase in the current gain is due to which regenerative action may tend to unity and thyristor may be turned on. This type of turn-On may cause a thermal runaway and is normally avoided.
2. Light Triggering: In this method, a light source is used to trigger the thyristor. A light-sensitive device such as a phototransistor is used to detect the light, which then generates a triggering pulse to turn on the thyristor. Light triggering is used in applications where isolation between the control circuit and the high-voltage circuit is required.
3. High Voltage: In this method, a forward voltage is applied to the anode of the thyristor with respect to the cathode, and the gate is left open. This causes a small amount of current to flow through the device, which triggers it into conduction.
4. RC Triggering (dv/dt): In this method, a resistor-capacitor (RC) network is connected between the gate and the cathode of the thyristor. When the voltage across the capacitor reaches the thyristor’s gate trigger voltage, the capacitor discharges through the gate terminal, triggering the thyristor into conduction.
5. Magnetic Triggering: In this method, a magnetic field is used to trigger the thyristor. A coil is wrapped around the thyristor, and when a current pulse is applied to the coil, a magnetic field is generated, which triggers the thyristor into conduction. Magnetic triggering is used in applications where isolation and high-speed switching are required.
6. Gate Triggering: If a thyristor is forward biased, the injection of gate current by applying a positive pulse voltage between the gate with respect to cathode terminals turned On the Thyristor. As the gate current is increased, the forward blocking voltage decreases and thus the thyristor is turned On. The gate-triggering method is widely used in power electronics because it provides precise control over the turn-on time of the thyristor.
Lastly, the turn-on process of a thyristor is crucial in controlling the flow of current in many electronic applications, including power electronics, motor control, and lighting control, among others.
Hope you Understand. If not please feel free to comment down below.