The following are the important terms much used in the circuit breaker analysis:
- Arc Voltage:- It is the voltage that appears across the contacts of the circuit breaker during the arcing period.
As soon as the contacts of the circuit breaker separate, an arc is formed. The voltage that appears across the contacts during the arcing period is called the arc voltage. Its value is low except for the *period the fault current is at or near zero current point. At current zero, the arc voltage rises rapidly to peak value and this peak voltage tends to maintain the current flow in the form of an arc.
- Restriking voltage:- It is the transient voltage that appears across the contacts at or near current zero during the arcing period.
At current zero, a high-frequency transient voltage appears across the contacts and is caused by the rapid distribution of energy between the magnetic and electric fields associated with the plant and transmission lines of the system. This transient voltage is known as restriking voltage (Fig. 19.1).
The current interruption in the circuit depends upon this voltage. If the restriking voltage rises more rapidly than the dielectric strength of the medium between the contacts, the arc will persist for another half-cycle. On the other hand, if the dielectric strength of the medium builds up more rapidly than the restriking voltage, the arc fails to restrike and the current will be interrupted.
- Recovery voltage:- It is the normal frequency (50 Hz) r.m.s. the voltage that appears across the contacts of the circuit breaker after final arc extinction. It is approximately equal to the system voltage.
When contacts of the circuit breaker are opened, the current drops to zero after every half cycle. At some current zero, the contacts are separated sufficiently apart and the dielectric strength of the medium between the contacts attains a high value due to the removal of ionized particles. At such an instant, the medium between the contacts is strong enough to prevent the breakdown by the restriking voltage.
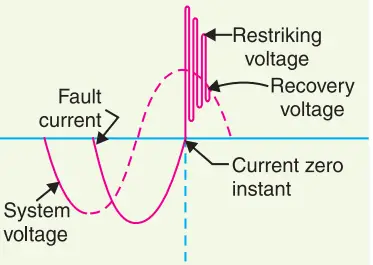 Consequently, the final arc extinction takes place and the circuit current is interrupted. Immediately after the final current interruption, the voltage that appears across the contacts has a transient part (See Fig. above). However, these transient oscillations subside rapidly due to the damping effect of system resistance and normal circuit voltage appears across the contacts. The voltage across the contacts is of normal frequency and is known as recovery voltage.
Consequently, the final arc extinction takes place and the circuit current is interrupted. Immediately after the final current interruption, the voltage that appears across the contacts has a transient part (See Fig. above). However, these transient oscillations subside rapidly due to the damping effect of system resistance and normal circuit voltage appears across the contacts. The voltage across the contacts is of normal frequency and is known as recovery voltage.








