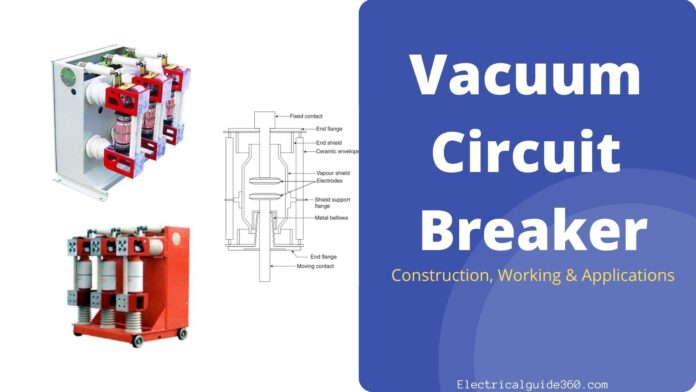
We all know that the circuit breaker is an electrical switching device that is used for protecting the power system when any type of fault occurs. It is automatically operated at any instant of time without doing it manually. Now, Vacuum Circuit Breaker or VCB is one type of circuit breaker that is used for the protection of power systems during system abnormality.
Let’s discuss and learn more about it below…
What is a Vacuum Circuit Breaker?
By Definition: A circuit breaker that uses a vacuum medium for arc extinction is called a Vacuum Circuit Breaker or VCB. Sometimes it is known as a vacuum interrupter.
Vacuum Circuit Breaker or VCB is one of the most reliable and superior circuit breakers among all the other circuit breakers. It can be operated at a high voltage system.
In a circuit breaker like porcelain, oil, air, and SF6 the dielectric strength and arc interrupting ability are considerably low as compared to that of a Vacuum Circuit Breaker. This means arc in these (porcelain, oil, air, and SF6) circuit breakers are formed due to the ionized molecules of a surrounding medium. But, in vacuum circuit breaker arc formation cannot take place due to the absence of liquid and gaseous molecules. Thus, it is reliable and commonly used.
[Note that small arc formation is considerable but excessive arc formation can damage the equipment and have poor performance]
How do Electrical Vacuum Circuit Breakers Works?
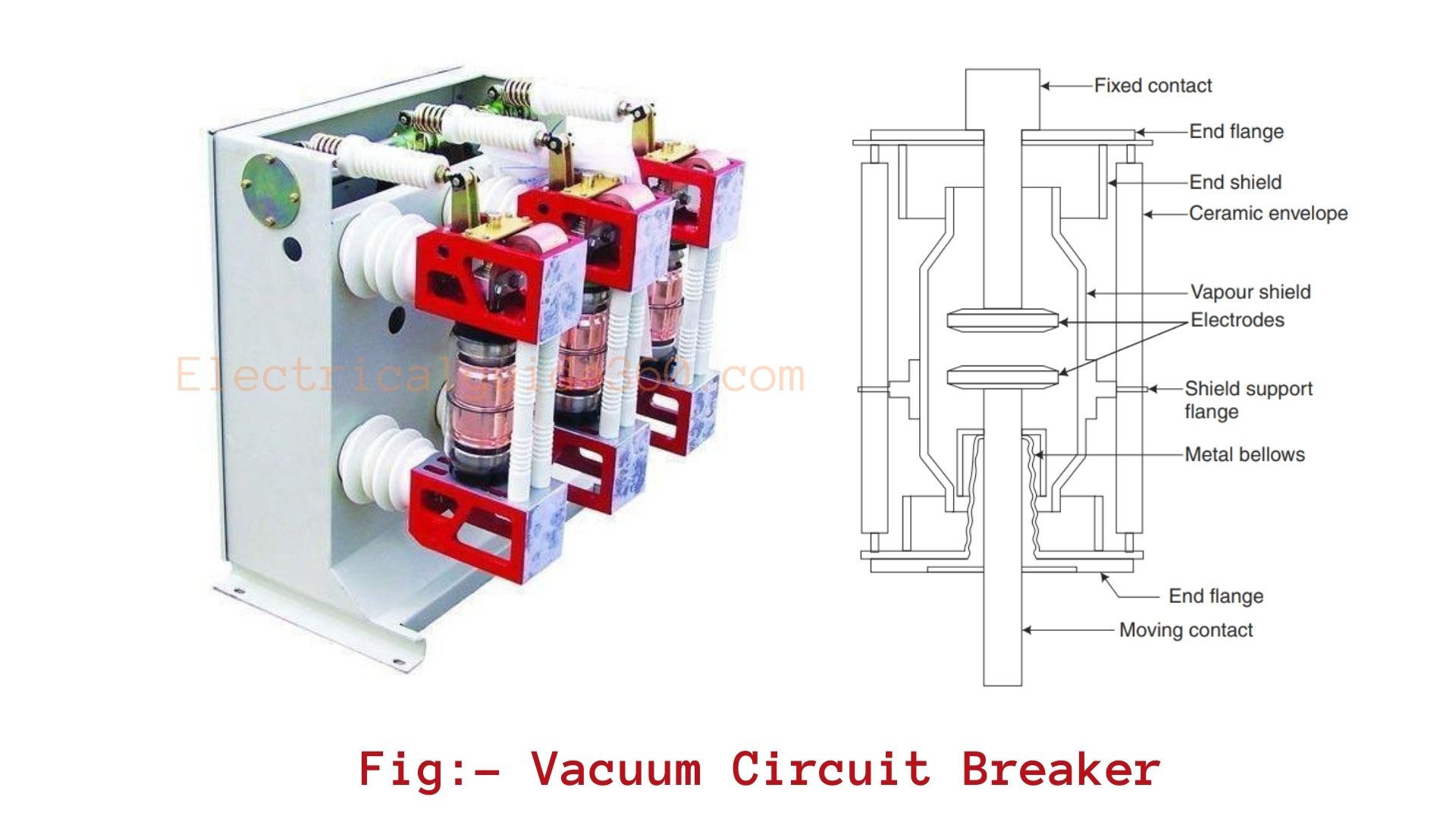
The working principle of a vacuum circuit breaker (VCB) is to isolate the contact when faults occur in the system and to extinguish the arc generated within the vacuum, during the operation.
When the fault occurs in the system, the circuit breaker opens its contact in order to isolate the system as faster as possible. Now, during this operation, the arc is generated because of the metal vapors ionization in the contacts. Also, in other words, the temperature is too high in the connecting parts due to which there occurs an ionization.
This arc generated can be quickly stopped or extinguished as electrons, ions & metallic vapors are condensed in the contact surface which makes a quick improvement rate in the dielectric strength of the vacuum.
The working of the Vacuum Circuit Breaker depends on the stored-energy mechanism in the closing spring. Closing spring can be done electrically or manually and it is charged automatically after the operation.
Finally, the tripping is done after detecting high voltage in the system thereby breaking the contact to isolate the system.
Also Learn: What is Electromagnetic Relays? Working Principle & Types
Construction of Vacuum Circuit Breaker
The figure below shows the construction of a vacuum circuit breaker. The covering part of the vacuum circuit breaker is made of insulating material such as glass, porcelain, or glass fiber reinforced plastic. Mostly glass material is used because it helps to in observation from the outside, and if the glass is blur-like then it simply indicates that the breaker is losing its vacuum. 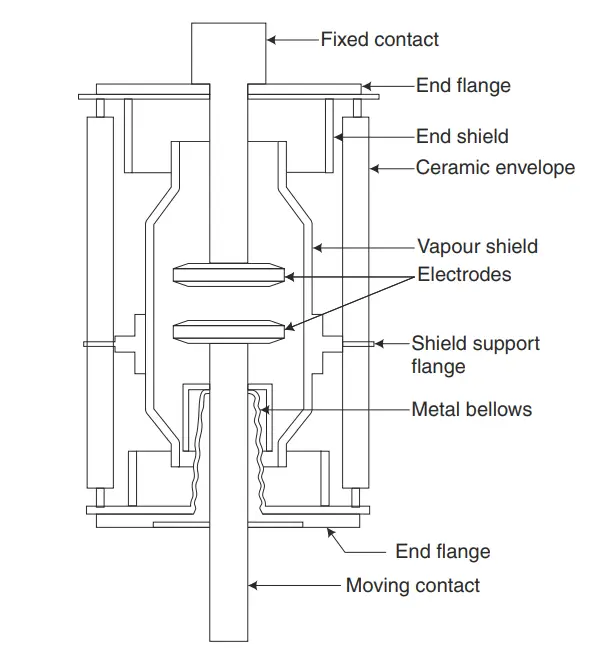 As shown in the figure, the upper contact in which the electrode is attached is fixed or is welded. And, the lower contact has been sealed with a stainless metallic bellow design as a moving object.
As shown in the figure, the upper contact in which the electrode is attached is fixed or is welded. And, the lower contact has been sealed with a stainless metallic bellow design as a moving object.
Two metal end flanges are constructed. They support most of the circuit breakers such as fixed contact, outer insulating enclosure, vapor condensing shield, and metallic bellows. The contacts of the vacuum circuit breaker have large disc-shaped faces. The disc-shaped faces contain spiral segments so that the arc current produces an axial magnetic field.
The vacuum circuit breaker is very simple in construction compared to other types of circuit breakers. The separation between the two contacts is about 1 cm which is adequate for a current interruption in a vacuum. Vacuum circuit breakers have become popular due to voltage ratings up to 36 kV (In which they employ a single interrupter).
Advantages
- A vacuum circuit breaker requires less power for operation compared to other types of circuit breakers.
- It is capable of interrupting capacitive and small inductive currents, without producing excessive transient overvoltages.
- Suitability for repeated operations
- Requires Less maintenance.
- Silent operation.
- It is a reliable circuit breaker. It means arc extinguishes successfully all the time.
- High speed of dielectric recovery
- Less weight of moving parts, etc.
Disadvantages
- In Vacuum Circuit Breaker the cost will increase if the voltage exceeds 38kV.
- If there is a loss in the vacuum, the interrupter will totally fail to operate.
- Extra care needs to be taken for a chance of vacuum leakage.
Application
The uses of the vacuum circuit breaker are as follows:
- It is a high voltage circuit.
- Used at system voltage levels up to 72 kV.
- Used in power systems like substations and power generation systems.
- Generally, it is used for both indoor and outdoor purposes.
- It is used in railway applications for traction current and electric supply switching.
- It is used as a switching device where motor drives are employed.
Frequently Ask Question (FAQs)
- What is a vacuum circuit breaker used for?
Answer:- Vacuum circuit breakers are more commonly used at system voltage levels up to 72 kV. Because arc cannot occur because there is no gas to ionize the contact surrounding, the insulating gap is smaller than in other circuit breakers.
- What is the working principle of VCB?
Answer:- Vacuum circuit breaker or VCB works when the current exceeds its rated value. In other words, the circuit breaker will be operated if there is an overload current in the system. Inside the circuit breaker, it is a vacuum, therefore arc formation within the circuit breaker is totally extinguished and cannot occur due to the absence of moisture or ionization particles.
- What is the difference between an air circuit breaker and a vacuum circuit breaker?
Answer:- The difference between an air circuit breaker and a vacuum circuit breaker is shown in the table below:
Descriptions | Vacuum Circuit Breaker (VCB) | Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) |
Voltage Application | MV (Medium Voltage) from 11kV up to 33 kV | LV voltage application upto 690 Volts 50Hz/60 Hz |
Arc Quenching Medium | Vacuum | Air |
Working Principle | Free electron cannot be formed in vacuum, Since the vacuum filled In between the male and female contact. Whenever the circuit breaker interrupts, the arc will be quenched by vacuum. | Air act as a good dielectric medium. Since moving and fixed contact are kept in open air with closed package. Whenever the circuit breaker opens, the arc will be quenched by air |
Rating of the circuit breaker | From 1250 to 4000A | Form 630 A to 6300A |
Arc Development | Less | High |
Maintenance | Very rare, once installed means VCB works like any thing. | Maintenance |
- What is the most serious problem in vacuum circuit breakers?
Answer:- The most serious problem that can occur in VCB is the amount or the degree of vacuum inside the circuit breaker reduces due to which the circuit breaker fails to operate.
- How do you check the vacuum on the vacuum breaker?
Answer:- You check the vacuum on the vacuum breaker using three tests: (1)contact resistance test, (2) high potential withstand test, and (3) The leak-rate test.
Also, you can check by observing it from the outside, if the enclosed glass looks blurry compare to the initial time, then you can say that the degree of vacuum inside the breaker is reduced.
- How vacuum is maintained in a vacuum circuit breaker?
Answer:- Vacuum in Vacuum circuit breaker is maintained as it is sealed closely. However, there may be a leakage in some way. That is why it is necessary to inspect and observe the vacuum concentration regularly.