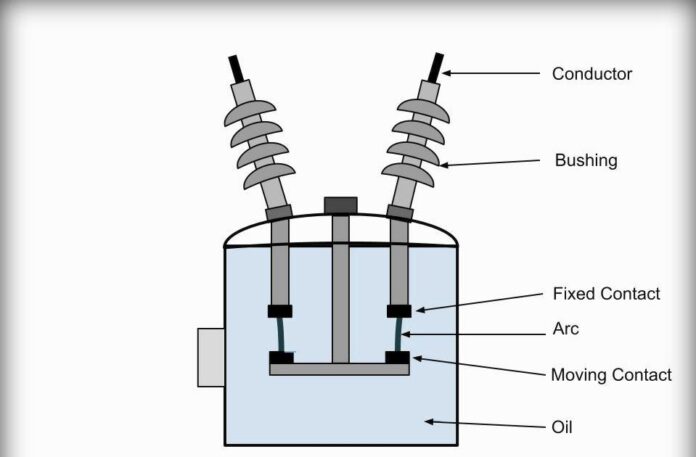
In such circuit breakers, some insulating oil (e.g., transformer oil) is used as an arc quenching medium. The contacts are opened under oil and an arc is struck between them.
The heat of the arc evaporates the surrounding oil and dissociates it into a substantial volume of gaseous hydrogen at high pressure. The hydrogen gas occupies a volume about one thousand times that of the oil decomposed. The oil is, therefore, pushed away from the arc and an expanding hydrogen gas bubble surrounds the arc region and adjacent portions of the contacts (See Fig. below).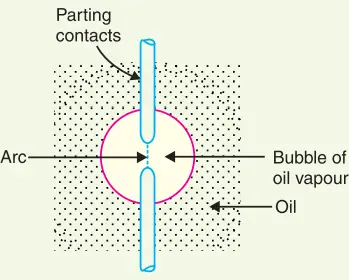
The arc extinction is facilitated mainly by two processes. Firstly, the hydrogen gas has high heat conductivity and cools the arc, thus aiding the de-ionization of the medium between the contacts. Secondly, the gas sets up turbulence in the oil and forces it into the space between contacts, thus eliminating the arcing products from the arc path. The result is that the arc is extinguished and the circuit current interrupted.
Types of Oil Circuit Breakers
The oil circuit breakers find extensive use in the power system. These can be classified into the following types:
(i) Bulk oil circuit breakers that use a large quantity of oil. The oil has to serve two purposes. Firstly, it extinguishes the arc during the opening of contacts and secondly, it insulates the current-conducting parts from one another and from the earthed tank. Such circuit breakers may be classified into:
(a) Plain break oil circuit breakers (b) Arc control oil circuit breakers.
In the former type, no special means are available for controlling the arc and the contacts are directly exposed to the whole of the oil in the tank. However, in the latter type, special arc control devices are employed to get the beneficial action of the arc as efficiently as possible.
(ii) Low oil circuit breakers which use the minimum amount of oil. In such circuit breakers, oil is used only for arc extinction; the current-conducting parts are insulated by air or porcelain, or organic insulating material.
Advantages
The advantages of oil as an arc quenching medium are:
- It absorbs the arc energy to decompose the oil into gases that have excellent cooling properties.
- It acts as an insulator and permits smaller clearance between live conductors and earthed components.
- The surrounding oil presents a cooling surface in close proximity to the arc.
Disadvantages.
The disadvantages of oil as an arc quenching medium are:
- It is inflammable and there is a risk of a fire.
- It may form an explosive mixture with air
- The arcing products (e.g., carbon) remain in the oil and their quality deteriorates with successive operations. This necessitates periodic checking and replacement of oil.
Maintenance of oil circuit breaker
The maintenance of an oil circuit breaker is generally concerned with the checking of contacts and dielectric strength of the oil. After a circuit breaker has interrupted fault currents a few times or load currents several times, its contacts may get burnt by arcing and the oil may lose some of its dielectric strength due to carbonization. This results in the reduced rupturing capacity of the breaker.
Therefore, it is a good practice to inspect the circuit breaker at regular intervals of 3 or 6 months. During an inspection of the breaker, the following points should be kept in view:
- Check the current-carrying parts and arcing contacts. If the burning is severe, the contacts should be replaced.
- Check the dielectric strength of the oil. If the oil is badly discolored, it should be changed or reconditioned. The oil is in good condition and should withstand 30 kV for one minute in a standard oil testing cup with a 4 mm gap between electrodes.
- Check the insulation for possible damage. Clean the surface and remove carbon deposits with a strong and dry fabric.
- Check the oil level.
- Check the closing and tripping mechanism.
Reference Book: Principles of power systems vk-mehta










Hello there,
when we want to do maintenance of our ACB, we clean up all the dust and lubricants from the moving and fixed contacts for better performance. and here in Oil CB the contacts are in the lubricants (oi) all the time specially the surface of the contact is lubricated, So does the current flow when the surfaces of both (fixed and moving) contacts are lubricated?
Thanks.
No. The current will not flow.
The lubricating properties of the oil are not meant to facilitate current flow between the contacts. In fact, the oil is there primarily as an insulator and quenching medium. The lubrication properties of the oil are secondary and help reduce friction between the moving and fixed contacts during the opening and closing operations.