Definition: The loading effect is the effect to which a measurement instrument impacts electrical properties like the voltage, current, and resistance of a circuit. In other words, the Loading effect can be defined as the effect on the source by the load impedance. Usually loading effect reduces the voltage level of a voltage source.
To understand clearly, you should know that the loading effect includes two things: First, the power that is consumed by the resistance of instrument circuits (measurements) itself, and secondly, the power which is consumed by the resistance of the main load. These two conditions describe the overall loading effects.
In this topic, we will discuss the ‘loading effect’ that takes place on various measurements like the loading effect in voltmeter, ammeter, and transducer.
Also see: 150+ V. Important Synchronous Motor MCQ Questions and Answers.
1. Loading effect of Voltmeter
A sensitivity rating is very important when selecting a meter for a particular measurement. It is to be noted that, If the circuit of a sensitive meter has low resistance, then it is more likely that the reading will come accurate. But if the resistance of the circuit of measurement instruments is high, then the reading is more likely to be inaccurate. It is because as discussed above, high resistance will consume more power thus obtaining inaccurate results of the circuits.
Suppose, A voltmeter is connected across the low resistance circuit that is to be measured. As the resistance of the voltmeter is low, the maximum current will flow through the low resistance circuit and will produce a voltage drop giving out a true reading.
In another case, If a voltmeter is connected across the high resistance circuit, the current flow will be divided (maybe equally) across the circuits as the resistance of the voltmeter is also high. Thus, there will be a voltage drop and will result in a much lower value reading than the original values.
From the above cases, it can be concluded that…
The loading effect of the voltmeter is the effect or the change between the actual voltage that is present in the circuit without connecting the voltmeter and the voltage that appears in the circuits after connecting the voltmeter.
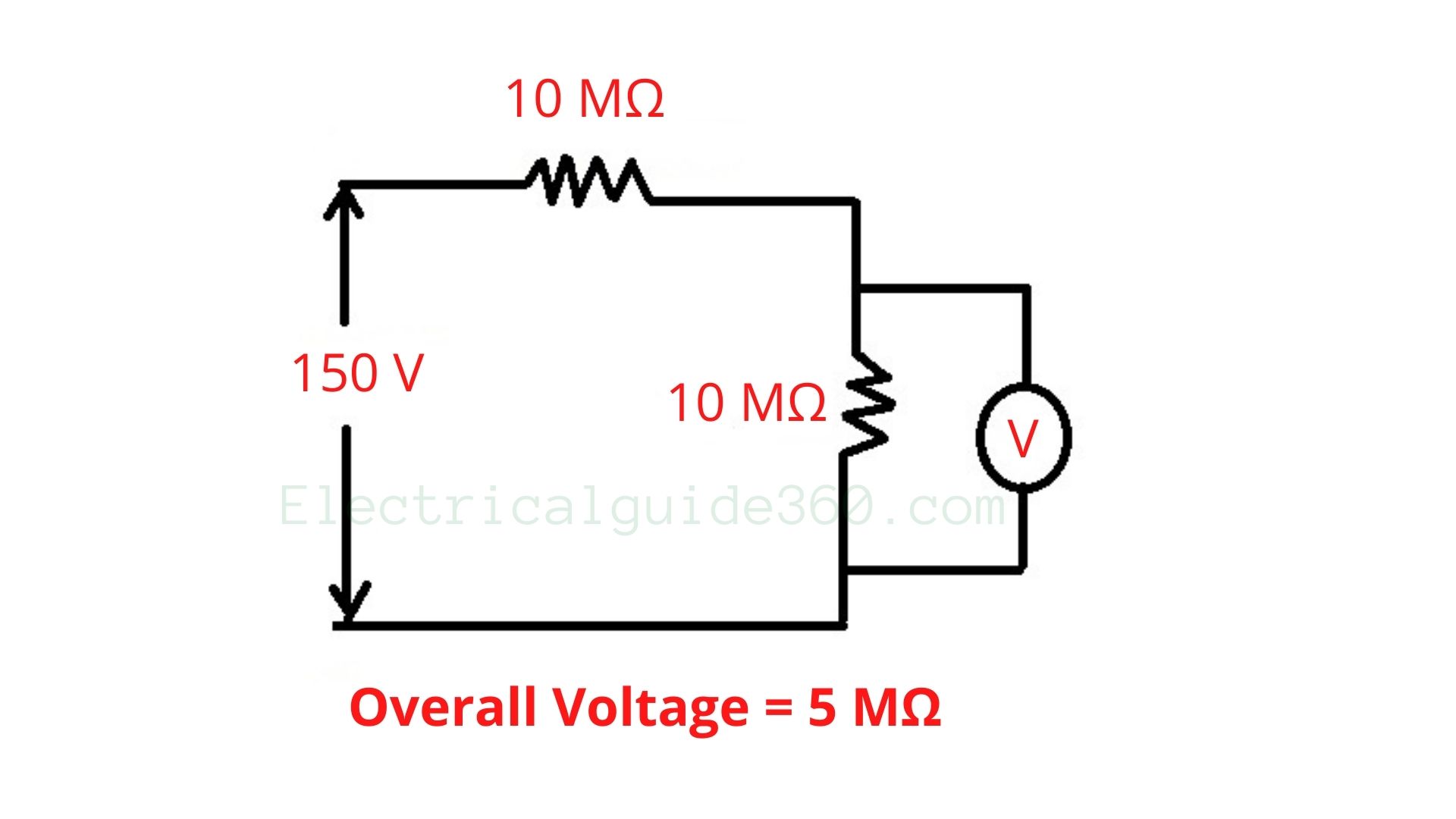
For example:- In figure (a), When a voltmeter with 10 MΩ internal resistance is connected in parallel to 10 MΩ resistors, the overall change in resistance will be 5 MΩ. The resistance will bring an impact on the value of voltage. This effect is known as the loading effect in voltmeter.
2. Loading effect of Ammeter
Sensing elements of most ammeters use very low-value resistance. The practical ammeter is built with a very small value (10Ω-100Ω). Now, the ammeter is connected in series with the circuits to measure the flow of current.
This will add extra resistance to the circuits. Thus, it will alter the circuit conditions in a small way. This little impact or change in the value of current is known as the loading effect.
A good quality ammeter will have low-value internal resistance whereas a low-quality ammeter will have higher internal resistance. Low internal resistance will have higher accuracy than high internal resistance.
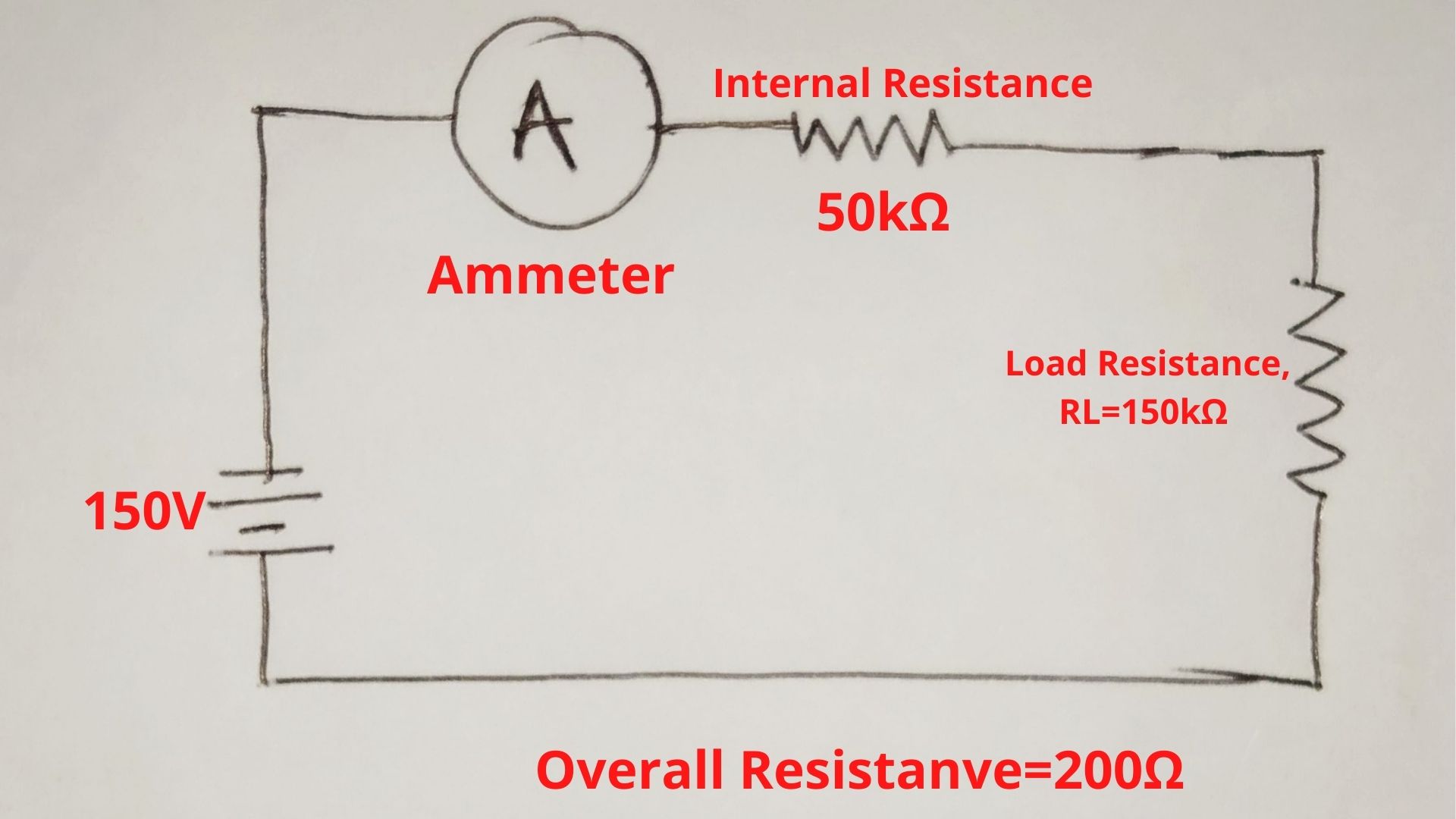
Example:- In Figure (b), When an ammeter with 50Ω internal resistance is connected to circuits that have 150Ω resistance. The overall resistance becomes 200Ω. The overall resistance is four times the internal resistance of the ammeter. So, it will also bring impact to current and voltage value by 4 times. This effect or impact is known as the loading effect in the ammeter.









These two statements certainly appear contradictory:
(from 1st para. under heading “1. Loading effect of Voltmeter”):
“But if the resistance of the circuit of measurement instruments is high, then the reading is more likely to be inaccurate.”
(from 2nd para.)L
“As the resistance of the voltmeter is high, the maximum current will flow through the low resistance circuit and will produce a voltage drop giving out a true reading.”
In the first quoted text, the high resistance of the measurement instrument is said to give an inaccurate reading, while in the second quoted text, the measurement instrument’s high resistance is said to give a “true reading”
True. We have updated it and written it as ‘Low Resistance’…