The conversion of energy available in different forms in nature into electrical energy is known as the generation of electrical energy.
Electrical energy is a manufactured commodity like clothing, furniture, or tools. Just as the manufacture of a commodity involves the conversion of raw materials available in nature into the desired form, similarly electrical energy is produced from the forms of energy available in nature.
However, electrical energy differs in one important respect. Whereas other commodities may be produced at will and consumed as needed, the electrical energy must be produced and transmitted to the point of use at the instant it is needed. The entire process takes only a fraction of a second. This instantaneous production of electrical energy introduces technical and economical considerations unique to the electrical power industry.
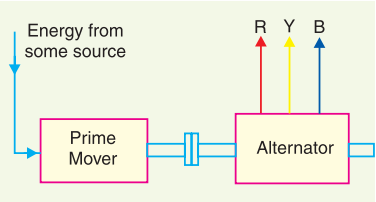
The forms of energy can be converted into electrical energy by the use of suitable arrangements. The arrangement essentially employs (see Figure above) an alternator coupled to a prime mover. The prime mover is driven by the energy obtained from various sources such as the burning of fuel, the pressure of water, the force of the wind, etc.
For example, the chemical energy of a fuel (e.g., coal) can be used to produce steam at high temperatures and pressure. The steam is fed to a prime mover which may be a steam engine or a steam turbine. The turbine converts the heat energy of steam into mechanical energy which is further converted into electrical energy by the alternator. Similarly, other forms of energy can also be converted into electrical energy by employing suitable machinery and equipment.
Let us now see the sources of energy…
Sources of Energy
Since electrical energy is produced from the energy available in various forms in nature, it is desirable to look into the various sources of energy. These sources of energy are :
(i) The Sun (ii) The Wind (iii) Water (iv) Fuels (v) Nuclear energy.
Out of these sources, the energy due by Sun and wind has not been utilized on large scale due to a number of limitations. At present, the other three sources viz., water, fuels, and nuclear energy are primarily used for the generation of electrical energy. It is to be noted that in this modern era, there are many more sources (renewable energy is another subject). In fact, among all those listed sources are the fundamental ones.
(i) The Sun.
The Sun is the primary source of energy. The heat energy radiated by the Sun can be focussed over a small area by means of reflectors. This heat can be used to raise steam and electrical energy can be produced with the help of the turbine-alternator combination.
However, this method has limited application because:
- It requires a large area for the generation of even a small amount of electric power
- It cannot be used on cloudy days or at night
- It is an uneconomical method.
Nevertheless, there are some locations in the world where strong solar radiation is received very regularly and the sources of mineral fuel are scanty or lacking. Such locations offer more interest to the solar plant builders.
(ii) The Wind.
This method can be used where wind flows for a considerable length of time. The wind energy is used to run the windmill which drives a small generator. In order to obtain the electrical energy from a windmill continuously, the generator is arranged to charge the batteries. These batteries supply the energy when the wind stops.
This method has the advantage that maintenance and generation costs are negligible. However, the drawbacks of this method are (a) variable output, (b) unreliable because of uncertainty about wind pressure, and (c) power generated is quite small.
(iii) Water.
When water is stored at a suitable place, it possesses potential energy because of the head created. This water energy can be converted into mechanical energy with the help of water turbines. The water turbine drives the alternator which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. This method of generation of electrical energy has become very popular because it has low production and maintenance costs.
(iv) Fuels.
The main sources of energy are fuels viz., solid fuel as coal, liquid fuel as oil, and gas fuel is natural gas. The heat energy of these fuels is converted into mechanical energy by suitable prime movers such as steam engines, steam turbines, internal combustion engines, etc.
The prime mover drives the alternator which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Although fuels continue to enjoy the place of chief source for the generation of electrical energy, their reserves are diminishing day by day. Therefore, the present trend is to harness water power which is more or less a permanent source of power.
(v) Nuclear energy.
Towards the end of the Second World War, it was discovered that a large amount of heat energy is liberated by the fission of uranium and other fissionable materials. It is estimated that heat produced by 1 kg of nuclear fuel is equal to that produced by 4500 tonnes of coal. The heat produced due to nuclear fission can be utilized to raise steam with suitable arrangements. The steam can run the steam turbine which in turn can drive the alternator to produce electrical energy.
However, there are some difficulties in the use of nuclear energy. The principal ones are (a) the high cost of nuclear plants (b) the problem of disposal of radioactive waste and the dearth of trained personnel to handle the plant.
Reference: Principles of power systems vk-mehta










