Armature windings have two types of winding i.e Lap Windings and Wave Windings. In this part, we will discuss lap winding and its types, constructions, formula, and calculations in detail.
What is Lap Winding?
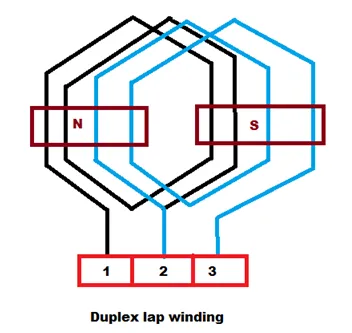
When the connections two coils overlap each other the windings are known as lap winding. Lap winding is preferred for a machine that has low voltage and high current as it has a number of parallel paths. In lap winding the number of brushes is always equal to the pole. A Diagram of lap winding is shown below:
In the figure above, there are two coils namely coil-1 and Coil-2. Here, the line is starting coil whereas the dotted lines are the finishing coil. Numbers 1, 2, and 3 are the segments of the commutator.
Now, In lap winding, the finishing coil of Coil-1 and starting coil of Coil-2 are jointly connected in the one segment of the commutator (segments no.2). It is to be noted that the starting coil of both Coil-1 and Coil-2 lies under the same pole (i.e N-pole) and the finishing coils lies under S-pole.
Types of Lap Windings
There are three types of Lap winding:
- Simple Lap Winding
- Duplex Lap Winding
- Triplex Lap Winding
Simplex Lap Winding
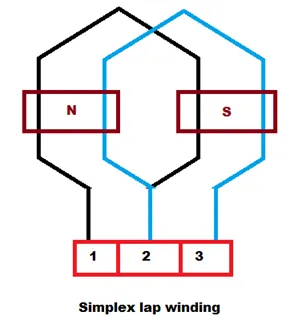 When the number of the parallel paths is equal to the number of poles then that type of winding is known as simplex Lap winding. For a simplex lap winding, the commutator pitch YC = 1 and coil span YS ~ pole pitch.
When the number of the parallel paths is equal to the number of poles then that type of winding is known as simplex Lap winding. For a simplex lap winding, the commutator pitch YC = 1 and coil span YS ~ pole pitch.
To understand, it simply means that one parallel path is in N-Pole and another parallel path in S-pole.
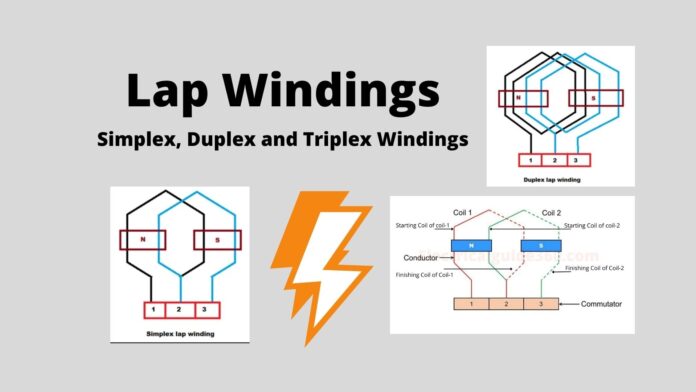
Duplex Lap Winding
When the parallel path is twice the number of poles then it is known as Duplex Lap Winding. This type of winding is mainly used for high current applications. Here, there are four successive coils of which two parallel paths will be under N-pole and another two parallel paths are under S-Pole.
Triplex Lap Winding
The triplex lap winding has a number of turns and is usually used for higher and larger currents. It is connected to one-third of the commutator bars. The only problem with this type of winding is that its coil cost will be more than other types of winding.
The formula of Lap Winding
If,
Z = the number of conductors
P = number of poles
YB = Back pitch
YF = Front pitch
YC = Commutator pitch
YA = Average pole pitch
YP = Pole pitch
YR = Resultant pitch
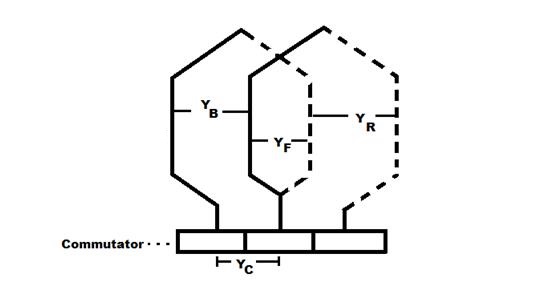
- Then, the back and front pitches are of opposite signs and they cannot be equal.
YB = YF ± 2m - m = multiplicity of the winding.
m = 1 for Simplex Lap winding
m = 2 for Duplex Lap winding - If, YB > YF, it is called progressive winding.
If, YB < YF, it is called retrogressive winding. - The equations of average pitch, pole pitch, and back pitch are given below:
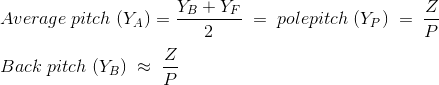
- The back pitch and front pitch must be odd.
- Resultant pitch (YR) = YB – YF = 2m
- YR is even because it is the difference between two odd numbers.
- Commutator pitch (YC) = ±m
- Number of the parallel paths in the Lap winding = mP
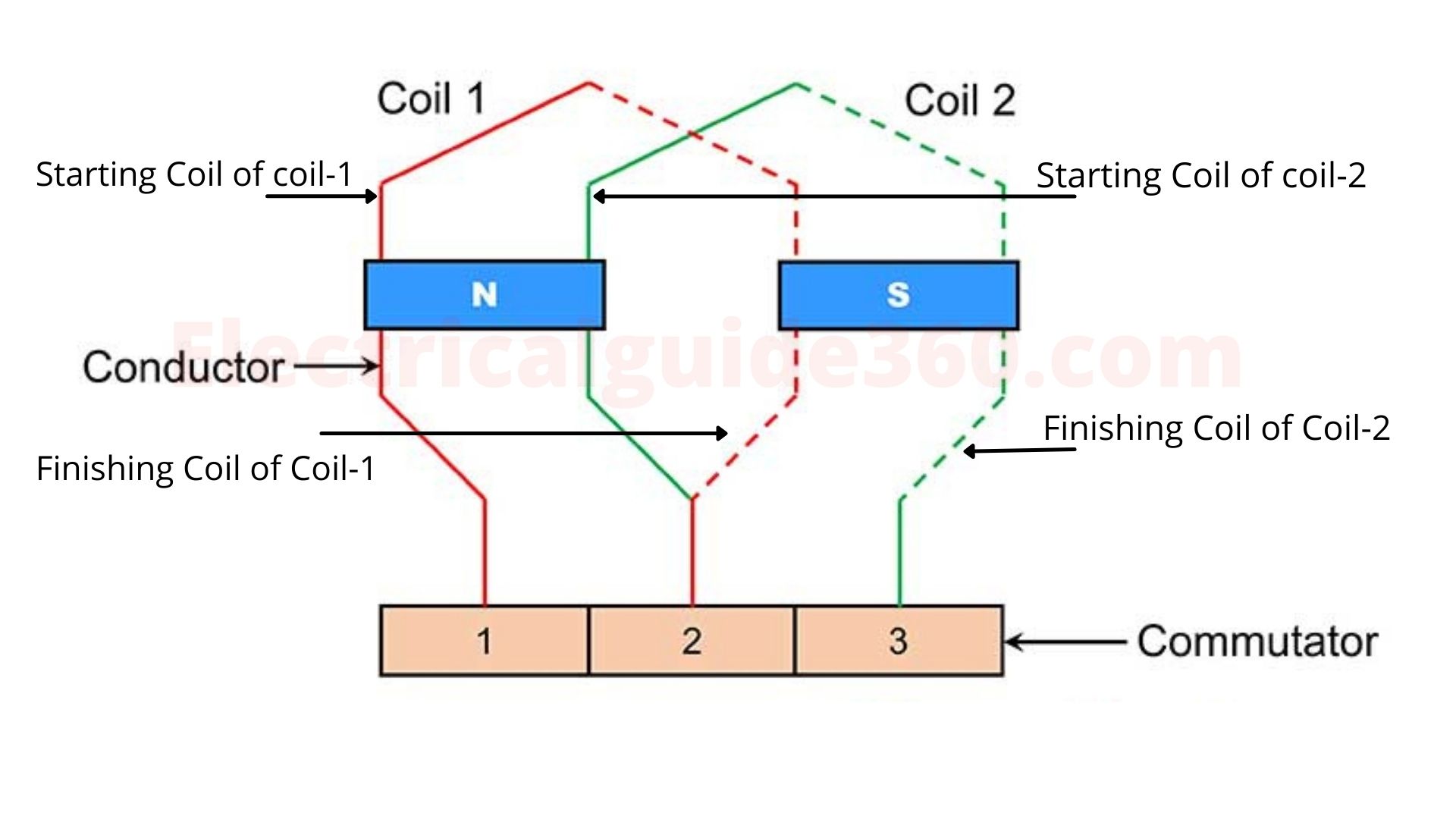
Calculations
Here, the table shows the calculation of lap winding from 1st conductor.