In domestic and industrial applications, motion control is required and is one of the most important factors. In a place like the transportation system, rolling mills, textile mills, fans, paper machines, pumps, and machine tools, etc. requires motion control. So, for this purpose, there needs to be a system to operate all the controls. This system employed for motion control is called Drives. And, any drives that involve an electrical appliance and system are known as electrical drives.
Definition: An electrical drives is an electromechanical system that is employed to control motion by controlling electrical energy supplied in an application. It is used for various industrial and domestic purposes.
Block Diagram
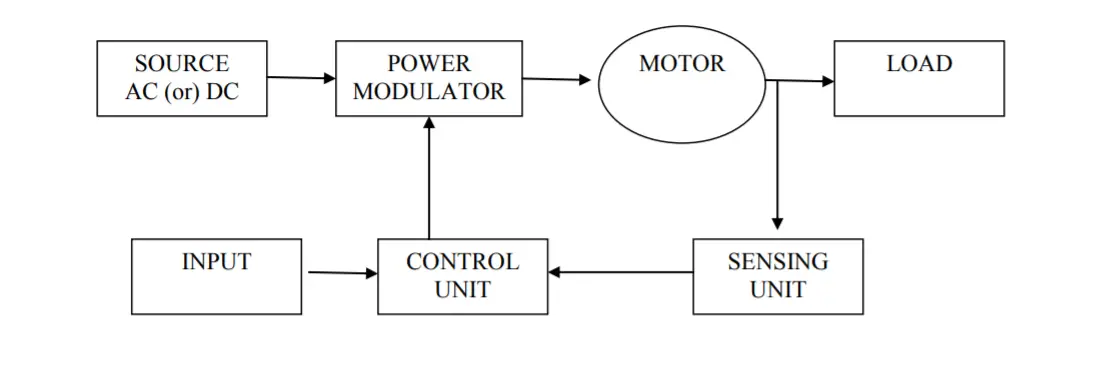
Parts of Electrical Drives
Still, confused? what are electrical drives? the answer is, all these parts of the drive such as the source, power modulator, motors, control unit, a sensing unit, and load are all the parts electrical drives system.
Let us now learn the functions of the parts of electrical drives.
(1) Source: Source may be either AC or DC. It is a place from where input is supplied to the drive system. In India, mostly 1-phase and 3-phase 50Hz ac supplies are used. Single-phase is used for very low power drives and 3-phase is used for moderate to high power drives. Most drives are supplied from an ac source or with the help of a converter.
(2) Power Modulator: Power Modulator is classified into three parts: (a) Converters; (b)Variable impedances, and (c) Switching circuits. [Note that out of all, a power modulator is most commonly used as a converter]
(a) Converters: The power modulators are used as the following converter:
1. Controlled rectifiers (AC to DC converters)
2. Inverters (DC to AC converters)
3. AC to AC converters (AC voltage controllers)
4. DC choppers (DC to DC converters)
5. Cycloconverters (frequency conversion)
(b) Variable impedances: It is commonly used for the control of low-cost dc and ac drives and is also needed for dynamic braking of drives.
(c) Switching Circuits: Sometimes power modulator is also used as a switching operation in order to disconnect the motor when an abnormality occurs in the system.
(3) Motor: Motors that are commonly used in electrical drives are:
- DC motors:- Shunt, Series, Compound, and Permanent Magnet.
- Induction motors:- Squirrel-cage motor, wound rotor, and linear.
- Synchronous motors:- Wound field and permanent magnet.
- Brushless dc motors, and
- switched reluctance motors.
(4) Load: It is a machine that is connected to the motors or we can say electrical drive system, in order to complete the given task.
(5) Sensing Unit: The sensing unit comprises torque-sensing, speed sensing, current, and voltage sensing, temperature sensing, and position sensing. It is required for protection purposes and closed-loop operations.
(6) Control Unit: The Control unit provides the signal and controls a power modulator. The nature of the control unit is based on the power modulator used. Here we have discussed only two cases.
Types of Electrical Drives
The types of electrical drives are classified on various bases.
(1) Based on Supply
- AC motor drives: AC drives are also known as adjustable speed drives, and variable speed drives(VSD), adjustable frequency drives. It is used to control the speed of motors by varying the frequency.
- DC motor drives: DC drives are used to convert ac into dc. DC drives have high start-up torque – which is useful in applications that require constant speed.
(2) Based on the number of motors
- Individual drive: Individual motors are used for each part of the machines. Example: Lathe.
- Multi-motor drive: In multi-motor drive, separate motors are used to operate and actuate the different parts of machines. Example: Cranes.
- Group drive: In group drive, one motor is used for two and more than two machines.
(3) Based on control Parameters
- Vector control drive: In vector control drives, the torque and speed of AC induction or synchronous motor are controlled by using PWM (Pulse width modulation).
- Constant power drive: At a certain range of speed if the armature of motors provides constant power, then it is a constant power drive.
- Constant torque drive: This type of drive is employed only when a fixed volume of the load is being handled.
(4) Based on the speed
- Constant speed drive: A constant speed drive or CSD is a device used in electromechanical drives in order to maintain a constant speed even though there is a varying input.
- Variable speed drive: It is a device used in electromechanical drives in order to control the torque and speed of an AC motor by varying the motor’s input voltage and frequency.
Applications
- Electrical drives are used in washing machines, lifts, cranes, lathes, boats, traction systems, electric cars, etc.
- Electrical drives are available in a wide range of speed, torque, and power.
- They can be started instantly at any time & can immediately be fully loaded as needed.
- The operation can be done in all four quadrants of the speed-torque plane.
- They can be operated in any conditions such as explosive and
radioactive environments.
Advantages
- Electric drives are comparatively low in cost compare to other types of drives in the market.
- It has high efficiency, has short time overloading capabilities, and has low no-load losses.
- Control is very easy and simple and easy to operate.
- It has a remote operating facility.
- They have flexible control characteristics.
- It can be started at any time without any delay.
- They are eco-friendly as compared to others.
- Transmission of power from one place to another can be done with the help of cables
instead of long shafts, etc.
Disadvantages
- It cannot be installed in the absence of electricity.
- Sometimes due to the machine’s sounds, it can cause noise pollution in the area.
- It has a poor dynamic response.
- During installation, its initial cost is comparatively high.
- In case of any electrical failure, it cannot be operated further.